Configuration management plays a central role in building reliable systems:
-
it safeguards sensitive information
-
it simplifies modifications to system settings
Approach 1: config file on local environment
In this configuration, the developer wants to handle all passwords without pushing them in the repo.
One can use an object Config. This object would have 2 class methods that load variables stored in a file config-dev.yaml.
# config.py
class Config:
@classmethod
def set_config_from_dict(cls, config_dict):
cls.certificate_path = config_dict['certificate_path']
cls.api_server = config_dict['api_server']
cls.api_key = config_dict['api_key']
def set_secrets_from_dict(cls, config_dict):
cls.api_key_secret = config_dict['api_key_secret']
# main.py
from config import Config
def assemble_config():
with open('config-dev.yaml') as f:
config = yaml.safe_load(f)
Config.set_config_from_dict(f)
Config.set_secrets_from_dict(f)
assemble_config()
Approach 2: config file on cluster environment
The idea here is to use a devops automation tool that has a variable substitution feature e.g. Octopus.
First, the developer has to write all configuration variables in the relevant project in Octopus. Then he writes a file values.yaml with reference to all configuration variable in the form “#{Icarus.API.Server}” (that way, no configuration variable is visible in the repo).
During deployment, Octopus will create a new file values.yaml with all configuration variables’ values.
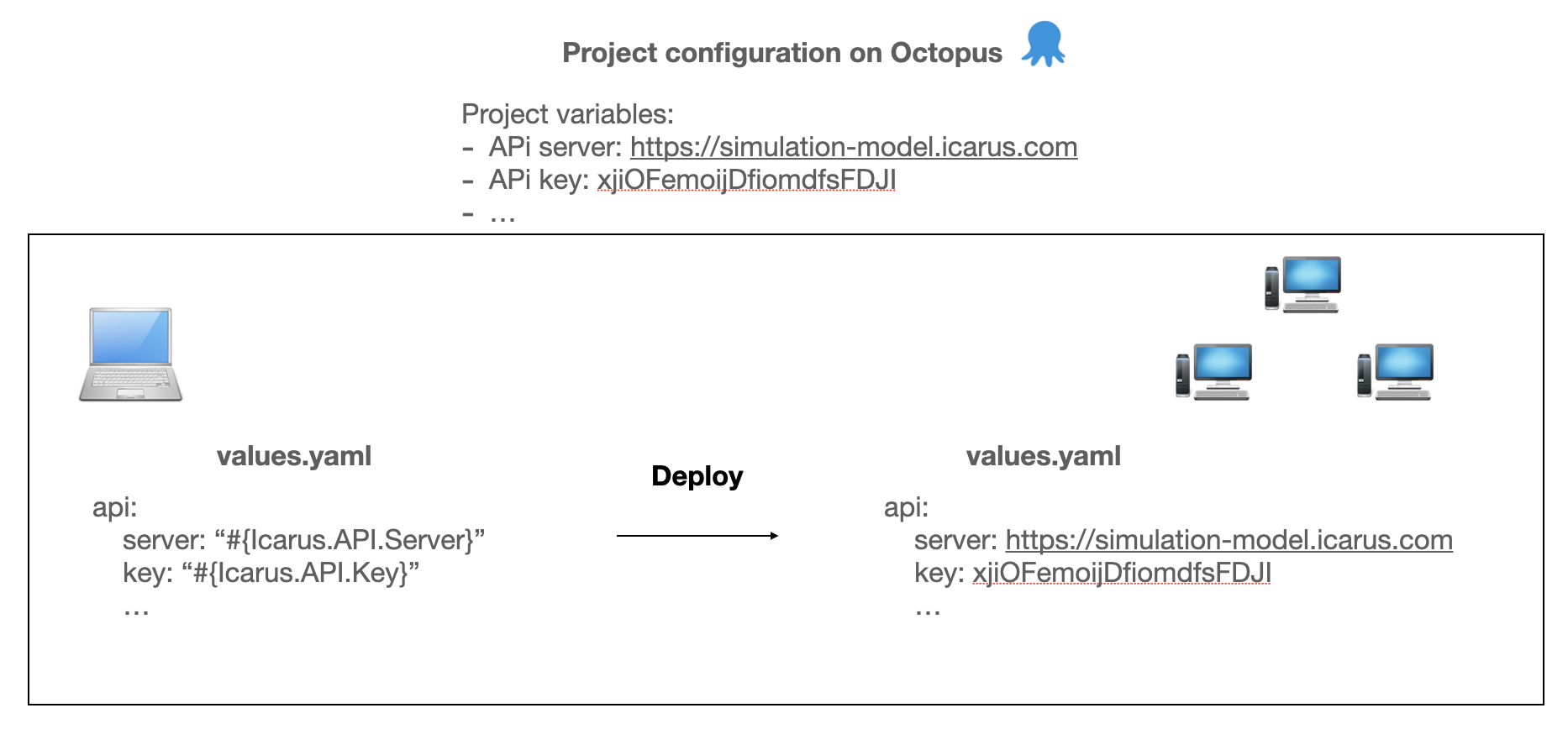
Once this setup is implemented, one can add two files configmap.yaml and secret.yaml that will generate two additional files config.yaml and secrets.yaml during deployment.
To load these files, one can use the same logic as approach 1 (using a Config object):
# main.py
from config import Config
def assemble_config():
with open('config.yaml.yaml') as f:
config = yaml.safe_load(f)
Config.set_config_from_dict(f)
with open('secrets.yaml') as f:
config = yaml.safe_load(f)
Config.set_secrets_from_dict(f)
assemble_config()
Alternatively, if the developer is using the Dependency Injection design pattern, the files can be loaded using the property .from_yaml.
# main.py
from containers import ApplicationContainer
def build_app() -> FastAPI:
app = FastAPI()
container = ApplicationContainer()
container.config.from_yaml('config.yaml')
container.config.from_yaml('secrets.yaml')
app.container = container
return app
build_app()